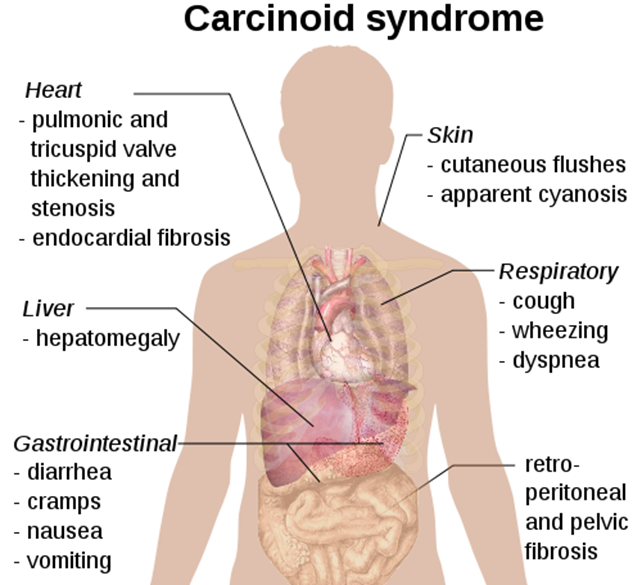
Carcinoid Syndrome:
Main vasoactive substances include:
- Serotonin
- Kallikrein (catalyzes the conversion of kininogen to bradykinin which is a powerful vasodilator and bronchoconstrictor)
- Histamine
If the primary tumor is from the GI tract (hence releasing serotonin into the hepatic portal circulation), carcinoid syndrome generally does not occur until the disease is so advanced that it overwhelms the liver's ability to metabolize the released serotonin.
Common Sites:
- Appendix (45%)
- ileum (30%)
- Rectum (20%)
- Other parts of GI tract, ovary, testis, and bronchi (5%)
Signs and symptoms
- Incidental Finding
- tumor-related symptoms
- carcinoid syndrome
- GI tumors can cause appendicitis, intussusception, or obstruction.
- Hepatic metastases may cause RUQ pain
- Pellagra
Diagnosis:
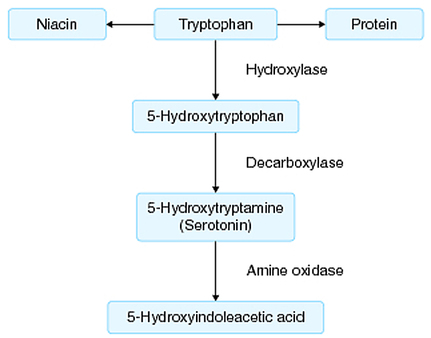
5-hydroxy-indole-acetic acid (5-HIAA)
- End product of serotonin metabolism
- Most useful initial test
- Measured in 24 hour urinary collection
- Patients with carcinoid syndrome usually excrete >25 mg of 5-HIAA per 24 hour
- Sensitivity 75% Specificity 100%
Chromogranin A (CgA)
- Present in wall of synaptic vesicles that store serotonin and glucagons
- Levels correlate with tumour bulk
- Elevated in 85-100% pts with carcinoid tumour
- Sensitivity 67.9% Specificity 85.7%
2. Imaging techniques
Conventional Imaging Modalities (CT, MRI, Ultrasound, Endoscopy) are used to locate tumors. Following scans can be performed to diagnose carcinoid tumors.
Octreoscan
- Initial imaging method for localization of both primary lesions and metastasis
- Indium-111 labelled somatostatin analogues (octreotide ) are used in scintigraphy for detecting tumors expressing somatostatin receptors.
- Detection rates with octreoscan are about 89%, in contrast to other imaging techniques such as CT scan and MRI with detection rates of about 80%
- Used to detect carcinoid and other neuroendocrine tumours
- Uses 123I- or 131I-labelled MIBG
- Useful for tumours which do not have somatostatin receptors
Treatment:
Octreotide (Sandostatin)
- somatostatin analogue which decreases the secretion of serotonin by the tumor
- Initial Treatment with solution: 100-600 mcg/day SC divided q6-12hr; may titrate up to 1500 mcg/day for 2 weeks
- Maintenance with Suspension (depot injection): 20 mg IM every 4 weeks
3. Chemotherapy (5-FU and doxorubicin)
4. Endovascular chemoembolization, targeted chemotherapy directly delivered to the liver through special catheters used for patients with liver metastases.






















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed





